U.S. Cybersecurity Agency Identifies and Adds Six Exploited Vulnerabilities to Known Flaws Catalog
U.S. Cybersecurity Agency Identifies and Adds Six Exploited Vulnerabilities to Known Flaws Catalog
Loading...

Ransomware is one of the frequent cyber threats which attack both companies and its private users. It works by the process of encrypting the files of the victims, make them available to access the files unless they have the key to it.
Researchers found the latest techniques which would help them to identify the dark web domains operating by the ransomware groups, and the techniques have been successfully executed to distinguish the unspecified infrastructure for the DarkAngels, Snatch, Quantum and Nokoyawa ransomware groups. These techniques are used against ransomware operators’ security failure, and to match the actor’s publicly indexed SSL certificate serial number and page elements.
Ransomware is one of the frequent cyber threats which attack both companies and its private users. It works by the process of encrypting the files of the victims, make them available to access the files unless they have the key to it.
Once accomplished in the system, ransomware encrypts your files and makes them inaccessible since it uses the most advanced forms of end-to-end encryption which is almost impractical to retrieve the affected systems without any decryption key.
Mainly, Ransomware operators are utilizing the dark web for their illegitimate activities such as distribution, affiliation, and collecting payment from victims with the help of Onion Router (TOR) which is considered to be the only medium to access the dark websites.
But the Threat actor’s improper usage of TOR and making configuration mistakes lead their activity to public, security researchers, or law enforcement agencies.
Since the Dark web domains are not globally indexed, Researchers adopted some of the following techniques to identify the ransomware operators for instance DarkAngels, Snatch, Quantum, and Nokoyawa ransomware groups hidden infrastructures.
TLS Certificate Matching
In this method of matching, researchers identified the self-signing certificate those are associated with the dark websites and matched it with the globally indexed webs to find whether it has any indication which is used on the public internet or not.
This TLS certificate matching method has been profitably applied and found the Dark Angels ransomware groups’ Dark web operations and their non-indexed TOR hidden service.
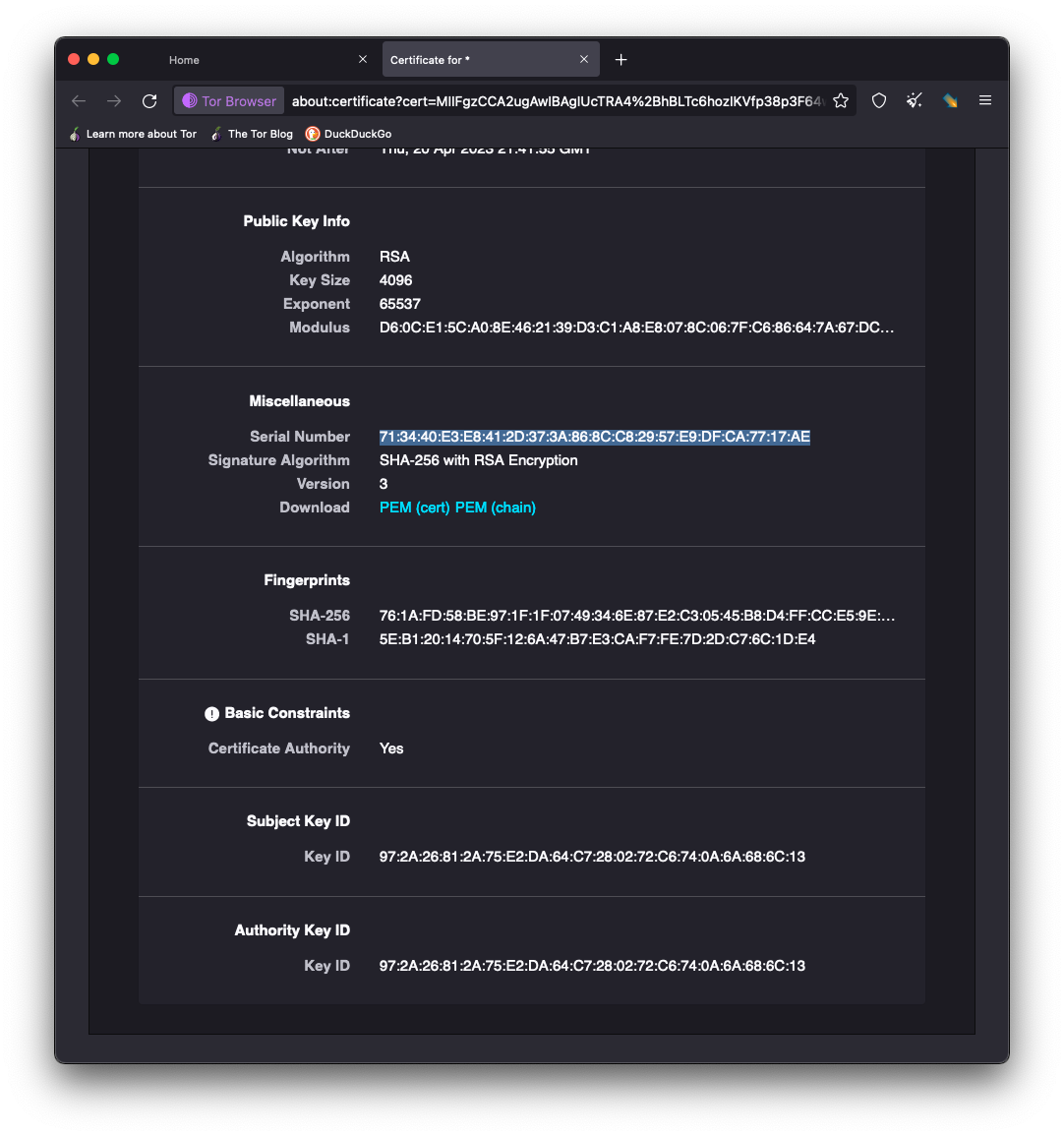
In the further analysis of this certificate matching, researchers have withdrawn the serial number from the TLS certificate and compared them with the web crawlers Shodan which catalogs TLS certificate information.
“By leveraging Shodan’s index, we discovered the same certificate that the DarkAngels actors have developed for themselves is also used by a host in Singapore with the IP address 89.38.225[.]166. According to whois.ripe.net, this above-mentioned host belongs to M247 LTD in Singapore (AS9009).” Disclosed by the Researchers.
Favicon Matching
Favicon is an icon which is related with the URL displayed in the address bar and serves as a visual branding badge for the web properties. In this case, alike the previous method, researchers indexed the public internet to check whether specific favicons on the dark web appear on the clear net as well. This perspective has been successfully worked to recognize the Quantum ransomware platoon to discover their dark web infrastructure which is hosted on the public internet. Later moment researchers found that the favicon file stored in the web root directory as favicon.ico from Quantum blog’s hidden service on TOR and also that they calculate the hash value.
Ultimately, Shodan discloses that the hash files matched with the indexed favicon file hash and acquires the clear web IP address of 185.38.185[.]32 which is being hosted in the Netherland.
Catastrophic Opsec Failures
Due to poor configuration, catastrophic security errors are formed that exposes their confidentiality. Ransomware operator fails to establish proper file permissions, and creates a strong directory traversal vulnerability which leads to find the exact ransomware admin location. With the help of this method, Researchers found the clues of Nokoyawa ransomware group which shares the code similarities with the Karma ransomware operation. By having access to this, victims can communicate with the affiliates to upload their files, and the ransomware operators decrypt the sample to prove the verification that their key works for the decryption.
In this care, researchers take the advantage of the affiliate’s catastrophic security mistakes and interfere with the files that leads to directory traversal attack.
“We found that the ransomware operators globally use hosting providers outside their country of origin (for instance Sweden, Germany and Singapore) to host their ransomware operation sites. They use VPS hop-points as a proxy which help to hide their true location when they connect to their ransomware web infrastructure for remote administration tasks.” The Researchers said.
U.S. Cybersecurity Agency Identifies and Adds Six Exploited Vulnerabilities to Known Flaws Catalog
In a stunning turn of events, a British individual has pleaded guilty to hacking the Twitter accounts of numerous celebrities in an attempt to steal Bitcoin. The high-profile case has sent shockwaves through both the cybersecurity and entertainment communities, highlighting the growing risks associated with digital currency and online platforms.
In a startling revelation, Western Digital, a leading data storage solutions provider, confirmed that it had fallen victim to a cyberattack in March, resulting in the theft of customer data. The breach, which took place earlier this year, has raised concerns about the security of personal information and the potential ramifications for affected individuals.
